Salesforce Triggers are very powerful. But if we write triggers without planning, the code becomes hard to manage, hard to debug, and risky in production.
That’s why we use a Trigger Framework.
A Trigger Framework helps us write clean, structured, and reusable trigger code.
What Is a Trigger Framework?
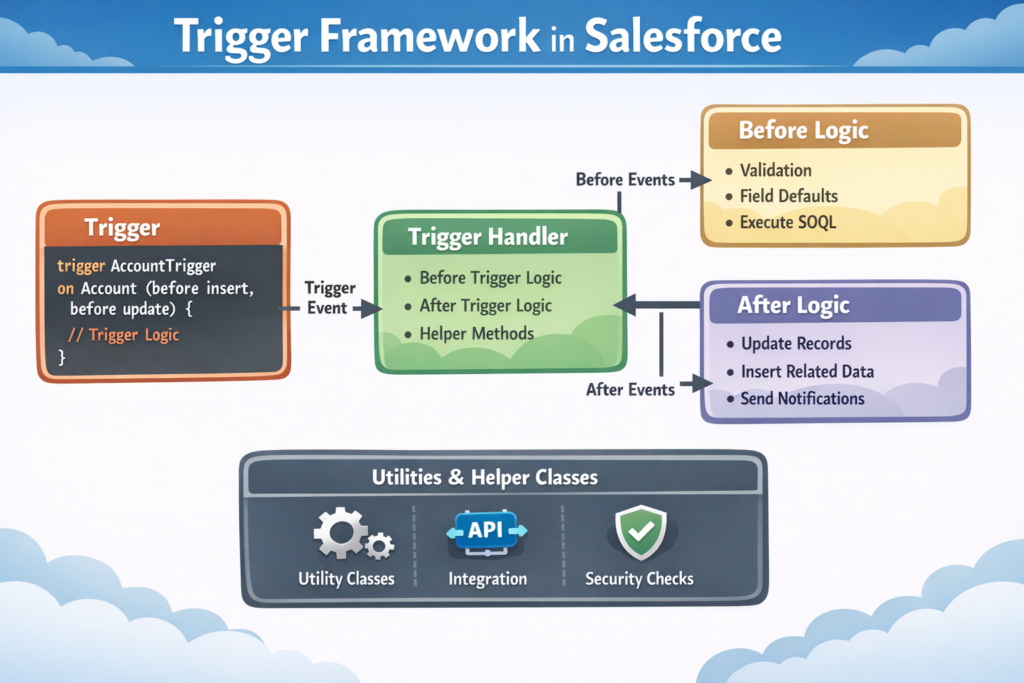
A Trigger Framework is a standard way of writing Salesforce triggers.
Instead of putting all logic inside the trigger:
-
The trigger only decides when to run
-
The real logic is written in Apex classes
👉 Think of the trigger as a switch, and the Apex class as the machine.
Why Do We Need a Trigger Framework?
Without a framework:
-
Code becomes messy
-
Same logic runs again and again
-
Debugging becomes difficult
-
Triggers fail in bulk data load
-
Governor limits are hit easily
With a framework:
-
Code is clean and readable
-
Easy to add new logic
-
Easy to test
-
Easy to control execution
Benefits of Trigger Framework
✔ Only one trigger per object
✔ No business logic inside trigger
✔ Bulk-safe code
✔ Easy debugging
✔ Prevents recursion (infinite loop)
✔ Easy maintenance
Important Rules of Trigger Framework
1. One Trigger Per Object
Always create only one trigger on each object.
Example:
-
Account → 1 trigger
-
Case → 1 trigger
2. Keep Trigger Simple
Trigger should:
-
Check the trigger event (before/after)
-
Call a handler class
❌ Logic in trigger
✅ Logic in Apex class
3. Separate Logic by Context
Different methods for:
-
Before Insert
-
Before Update
-
After Insert
-
After Update
-
Delete events
This makes code easy to read and manage.
4. Always Write Bulk-Safe Code
Triggers run on:
-
1 record
-
OR 200 records
So always:
-
Use lists and maps
-
Avoid SOQL/DML inside loops
5. Handle Recursion
Sometimes trigger runs again and again because of updates.
Use static variables to stop infinite loops.
Simple Trigger Framework Example
Step 1: Trigger (Very Simple)
Step 2: Trigger Handler Class
Why Use Handler Class?
Because:
-
Code is reusable
-
Logic is easy to change
-
Trigger stays clean
-
Testing becomes easy
Prevent Trigger from Running Again (Recursion Control)
Use it like this:
Disable Trigger When Needed
Useful during:
-
Data migration
-
Data loader
-
Integration
In trigger:
Trigger Framework vs Flow (Simple)
| When to Use | Trigger | Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Simple logic | ❌ | ✅ |
| Complex logic | ✅ | ❌ |
| Large data | ✅ | ⚠️ |
| Integration | ✅ | ❌ |
👉 Best practice: Use Flow first, Trigger when needed
Common Mistakes
❌ Writing logic in trigger
❌ Multiple triggers on same object
❌ SOQL inside loop
❌ No recursion control
❌ No test class
When Should You Use Trigger Framework?
You should use it when:
-
Project is big
-
Multiple developers work together
-
Data volume is high
-
Code must be long-term safe
Final Words
A Trigger Framework:
-
Makes your code clean
-
Saves time in future
-
Helps in interviews
-
Is required in real projects
If you want to grow as a Salesforce Developer or Architect, learning Trigger Framework is very important.