🌐 Inbound vs Outbound Web Services in Salesforce
When working with Salesforce integrations, one of the most important concepts is Web Services. They enable Salesforce to communicate with external systems, either by exposing its functionality for others to consume or by consuming services provided by other platforms.
These interactions are generally categorized into:
-
Inbound Web Services
-
Outbound Web Services
Let’s break this down in detail.
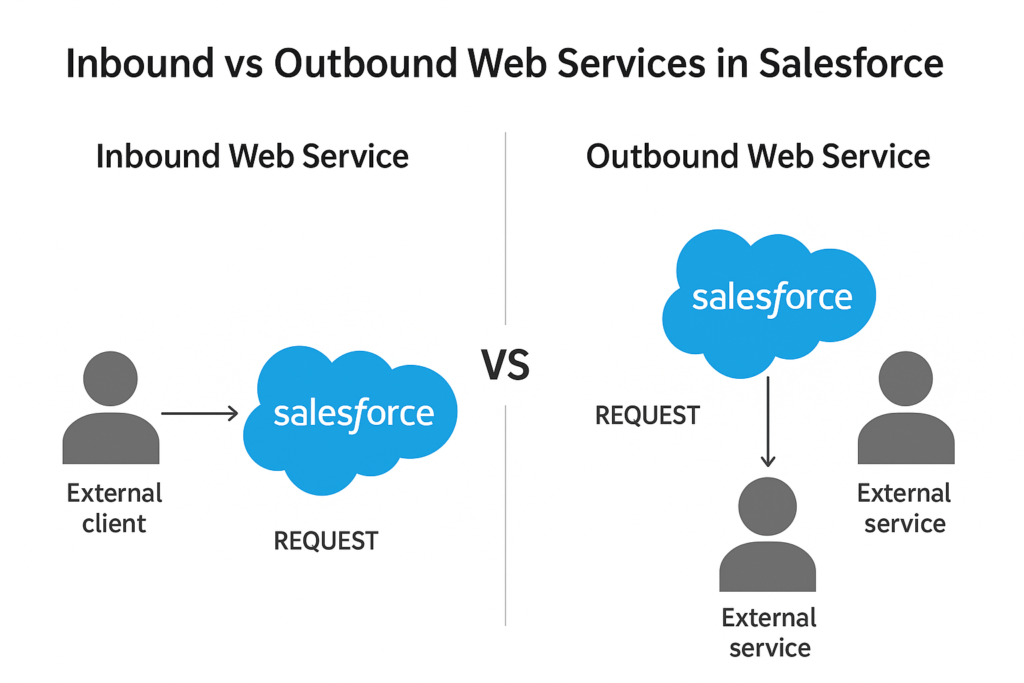
🔹 Inbound Web Services
Definition:
Inbound Web Services mean external systems call into Salesforce to either retrieve data or perform an operation. In this case, Salesforce is the service provider and the external application is the consumer.
How it works in Salesforce:
-
You can expose Apex classes/methods as web services.
-
These classes can be exposed as either SOAP or REST endpoints.
-
External systems then consume these services to perform operations like creating, updating, or fetching records from Salesforce.
Protocols supported for inbound web services in Salesforce:
-
✅ SOAP
-
By using the
webservicekeyword in Apex and WSDL (Web Service Definition Language). -
Example: Exposing an Apex class as a SOAP service.
-
-
✅ REST
-
By annotating Apex classes with
@RestResourceand methods with@HttpGet,@HttpPost, etc. -
Example:
/services/apexrest/YourService/endpoint
-
Use Case Example:
-
An eCommerce platform wants to create a new Lead in Salesforce whenever a customer registers.
-
The eCommerce system sends a REST call to Salesforce’s exposed
@RestResourceservice to insert the record.
🔹 Outbound Web Services
Definition:
Outbound Web Services mean Salesforce calls external systems to fetch or send data. Here, Salesforce acts as the consumer and the external system is the service provider.
How it works in Salesforce:
-
Salesforce makes callouts to external services.
-
This can be done using:
-
Apex callouts to REST APIs (using
HttpandHttpRequest). -
Apex callouts to SOAP services (using WSDL2Apex to generate stubs).
-
Protocols supported for outbound web services in Salesforce:
-
✅ SOAP
-
Supported via WSDL2Apex.
-
You upload a WSDL from the external service, and Salesforce generates Apex classes for making SOAP callouts.
-
-
✅ REST
-
Supported via Http callouts in Apex.
-
You construct an
HttpRequest, set headers and body, and make the callout to the external REST API.
-
Use Case Example:
-
Salesforce needs to fetch the latest currency exchange rates from an external REST API.
-
A nightly Scheduled Apex job makes a REST callout to the API and updates a custom object in Salesforce.
🔄 Quick Comparison
| Feature | Inbound Web Services (External → Salesforce) | Outbound Web Services (Salesforce → External) |
|---|---|---|
| Who initiates? | External System | Salesforce |
| Salesforce Role | Service Provider | Service Consumer |
| Protocols Supported | SOAP, REST | SOAP, REST |
| Examples | Exposing an Apex REST service for new Leads | Calling a payment gateway API for transactions |
| Tools in Salesforce | Apex webservice, @RestResource |
Apex Http, HttpRequest, WSDL2Apex |
🔑 Key Takeaways
-
Inbound Web Services → Salesforce exposes SOAP/REST services, external apps consume them.
-
Outbound Web Services → Salesforce consumes external SOAP/REST services via callouts.
-
Both SOAP and REST protocols are supported for inbound and outbound communication.
-
Always remember to configure Remote Site Settings or Named Credentials in Salesforce for outbound callouts.
-
Security (OAuth 2.0, basic auth, certificates) is critical in both inbound and outbound integrations.