Automation is a very important part of Salesforce. Tools like Flow and Process Builder help a lot, but sometimes they are not enough.
When you need:
-
complex logic
-
fixed-time execution
-
large data processing
-
background jobs
that is when Scheduled Apex and Cron Expressions are used.
In this blog, we will understand cron expressions in simple English, with easy examples and real use cases.
What Is a Cron Expression?
A Cron Expression is a time schedule written in a special format.
It tells Salesforce when to run a Scheduled Apex job.
In simple words:
A cron expression decides the exact time and date when your Apex code will run automatically.
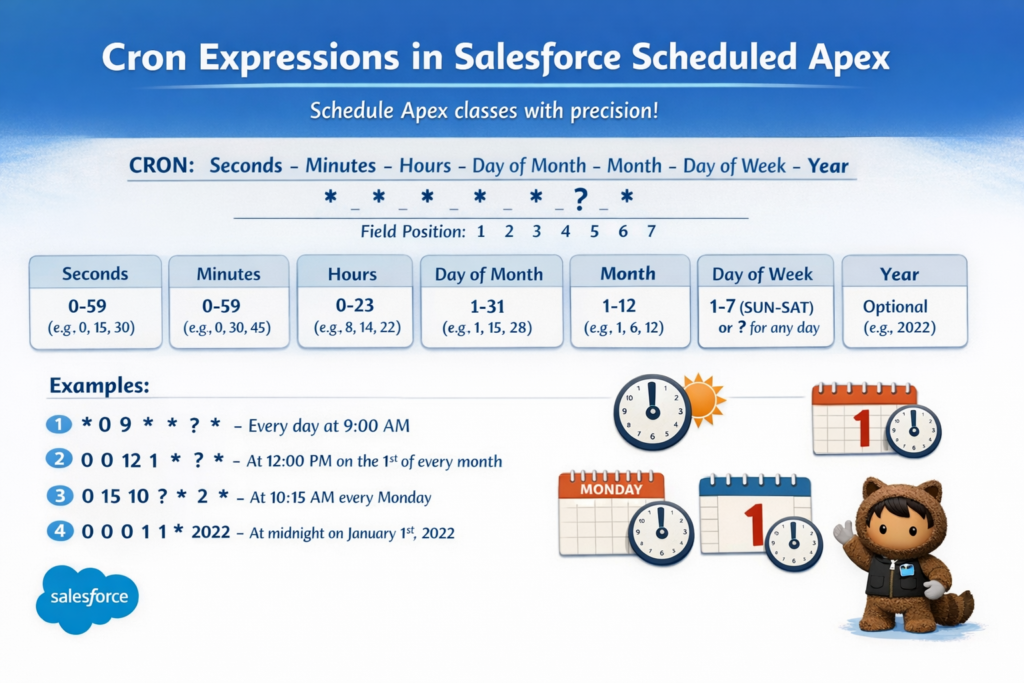
Salesforce cron expressions have 7 parts.
Salesforce Cron Expression Format
Each part controls one part of time.
Allowed Values in Salesforce Cron Expression
| Field | Allowed Values |
|---|---|
| Seconds | 0 – 59 |
| Minutes | 0 – 59 |
| Hours | 0 – 23 |
| Day of Month | 1 – 31 |
| Month | 1 – 12 or JAN – DEC |
| Day of Week | 1 – 7 or SUN – SAT |
| Year (Optional) | 1970 – 2099 |
⚠️ Important Rule:
You must use ? in either Day of Month or Day of Week.
You cannot use both at the same time.
Special Characters Used in Cron Expressions
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
* |
Every value |
? |
No specific value |
- |
Range (example: MON-FRI) |
/ |
Interval (example: every 15 minutes) |
, |
Multiple values |
Common Cron Expression Examples in Salesforce
| Requirement | Cron Expression | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Daily at 6 AM | 0 0 6 * * ? * |
Runs every day at 6 AM |
| Every Monday at 9 PM | 0 0 21 ? * MON * |
Runs every Monday night |
| First day of month | 0 0 1 1 * ? * |
Runs on 1st of every month |
| Every 15 minutes | 0 0/15 * * * ? * |
Runs every 15 minutes |
| Weekdays at 8 AM | 0 0 8 ? * MON-FRI * |
Monday to Friday at 8 AM |
When Should You Use Scheduled Apex?
Flows are good, but they have limits.
Use Scheduled Apex when:
-
Logic is too complex for Flow
-
You need to run code at a fixed time
-
Large data cleanup is required
-
Batch processing is needed
-
External system sync is required
Scheduled Apex gives more control and better performance.
Structure of a Scheduled Apex Class
To create a scheduled job:
-
Create a class that implements
Schedulable -
Override the
execute()method -
Schedule it using
System.schedule()
Example: Archive Inactive Cases Every Sunday at 3 AM
Let’s say we want to archive all cases that were closed more than 90 days ago, every Sunday at 3 AM.
Step 1: Create the Apex Class
Step 2: Schedule the Job Using Cron Expression
Run this code in Anonymous Apex:
Cron Expression Explanation: 0 0 3 ? * SUN *
-
0→ Seconds -
0→ Minutes -
3→ 3 AM -
?→ No day of month -
*→ Every month -
SUN→ Sunday -
*→ Every year
Real-World Use Cases of Scheduled Apex
| Use Case | Frequency | Cron |
|---|---|---|
| Data archiving | Weekly | 0 0 2 ? * SAT * |
| API sync | Daily | 0 30 1 * * ? * |
| Monthly reports | Monthly | 0 0 6 1 * ? * |
| Temporary data cleanup | Hourly | 0 0 0/1 * * ? * |
| ERP integration | Weekdays | 0 0 5 ? * MON-FRI * |
Salesforce Scheduled Apex Limits
| Limit | Value |
|---|---|
| Max scheduled jobs | 25 |
| Max concurrent async jobs | 5 |
| Max jobs per user | 100 |
To view jobs:
Setup → Scheduled Jobs
Best Practices for Scheduled Apex
-
Avoid hardcoding values
-
Use Custom Metadata or Labels
-
Monitor scheduled jobs regularly
-
Remove unused jobs
-
Add try-catch for error handling
-
Use Batch Apex for large data
Conclusion
Cron Expressions may look difficult at first, but once you understand them, they become very powerful.
Scheduled Apex helps you:
-
Automate tasks
-
Run jobs at fixed times
-
Handle complex logic
-
Improve system performance
For every Salesforce developer, learning Scheduled Apex and Cron Expressions is a must.