When working on Salesforce projects, especially real-world implementations, you will often deal with data that can relate to multiple objects. This is where polymorphic relationships come into the picture.
Many developers find polymorphic relationships confusing at first. But once you understand the concept and how to query them using SOQL, they become extremely powerful.
In this blog, we’ll break everything down in simple English, using real examples and use cases, so you can confidently work with polymorphic relationships in Salesforce.
What Is a Polymorphic Relationship in Salesforce?
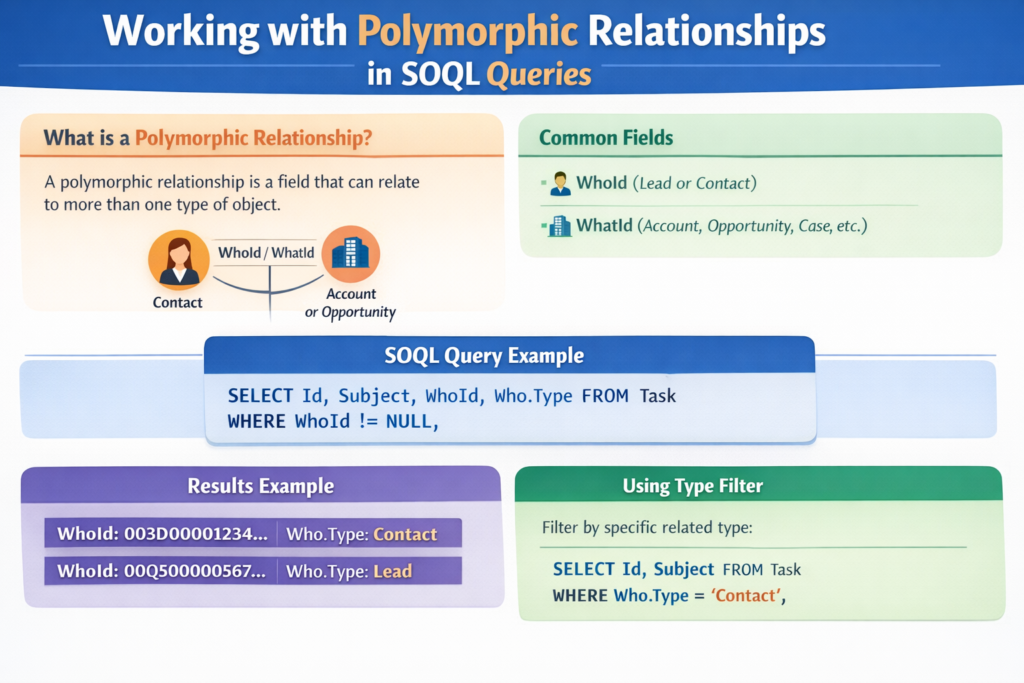
A polymorphic relationship is a relationship where one field can reference multiple objects instead of just one.
Simple Definition
A polymorphic relationship allows a single lookup field to point to different types of records.
Unlike a normal lookup field (which points to only one object), a polymorphic field can point to many different objects.
Best Real-World Example: Activities (Task & Event)
The most common polymorphic relationship in Salesforce is Activities.
Task & Event have two important polymorphic fields:
-
WhoId
-
WhatId
WhoId can refer to:
-
Lead
-
Contact
WhatId can refer to:
-
Account
-
Opportunity
-
Case
-
Custom Object
So instead of having separate lookup fields for each object, Salesforce uses one polymorphic field.
Why Salesforce Uses Polymorphic Relationships
Salesforce uses polymorphic relationships to:
-
Reduce complexity
-
Avoid multiple lookup fields
-
Support flexible data models
-
Handle real business scenarios easily
Imagine creating different lookup fields for Account, Opportunity, Case, etc.
That would be messy and hard to maintain.
Common Polymorphic Fields in Salesforce
| Object | Polymorphic Field |
|---|---|
| Task | WhoId, WhatId |
| Event | WhoId, WhatId |
| FeedItem | ParentId |
| Attachment | ParentId |
| ContentDocumentLink | LinkedEntityId |
| EmailMessage | RelatedToId |
How Polymorphic Relationships Work Internally
Each polymorphic field stores:
-
Record Id
-
Object Type (hidden)
Salesforce automatically understands which object the Id belongs to.
Example:
-
001XXXXXXXXXXX→ Account -
006XXXXXXXXXXX→ Opportunity -
003XXXXXXXXXXX→ Contact
Querying Polymorphic Relationships Using SOQL
Now let’s see how to work with polymorphic fields in SOQL.
Basic SOQL Query Example
Let’s say you want to fetch Tasks related to Accounts.
This query works, but it doesn’t tell you which object the task is related to.
Filtering by Object Type using TYPEOF
Salesforce provides a special keyword called TYPEOF to work with polymorphic fields.
Example: Fetch Tasks related only to Accounts
What’s happening here?
-
TYPEOFchecks the object type ofWhatId -
If it is an Account, it fetches Account fields
-
Other object types are ignored
TYPEOF with Multiple Objects
You can fetch data for multiple objects in a single query.
Example: Tasks related to Account and Opportunity
This is extremely useful in reporting and dashboards.
Querying WhoId (Lead or Contact)
Example: Fetch Tasks related to Contacts and Leads
This helps when building activity timelines or engagement dashboards.
Real-World Use Case 1: Activity Timeline
Scenario
You are building a custom activity timeline for a sales user.
Requirement
Show:
-
Task subject
-
Related record name (Account / Opportunity / Case)
Solution
Use polymorphic queries with TYPEOF to fetch everything in one query.
This avoids:
-
Multiple queries
-
Complex Apex logic
-
Performance issues
Real-World Use Case 2: Reporting & Analytics
Scenario
Management wants to know:
“How many activities are logged against Accounts vs Opportunities?”
Solution
Query Tasks using TYPEOF and group data based on object type.
This gives clean insights without creating multiple reports.
Real-World Use Case 3: Email & Attachments Tracking
Scenario
You want to fetch all attachments linked to:
-
Accounts
-
Cases
-
Opportunities
Query Example
This is useful for compliance, audits, and data cleanup.
Limitations of Polymorphic Relationships
While powerful, they have some limitations:
-
You cannot create custom polymorphic fields
-
You cannot use them in standard lookup filters
-
Reporting customization is limited
-
Cross-object formulas are not supported
Salesforce restricts them to standard objects only.
Best Practices While Working with Polymorphic Relationships
✔ Always use TYPEOF in SOQL
✔ Handle null values carefully
✔ Avoid unnecessary fields in queries
✔ Test queries with different object types
✔ Use selective filters for performance
Interview Tip (Very Important)
If asked:
“How do you handle polymorphic relationships in SOQL?”
Crisp Answer:
“Salesforce provides polymorphic fields like WhoId and WhatId which can reference multiple objects. We use the TYPEOF keyword in SOQL to identify the actual object type and fetch relevant fields dynamically.”
This answer shows real understanding, not just theory.
Final Thoughts
Polymorphic relationships are one of Salesforce’s most powerful yet misunderstood features. Once you understand how to query them properly using SOQL and TYPEOF, you can build:
-
Better reports
-
Faster Apex code
-
Cleaner UI components
-
Scalable enterprise solutions
If you’re working on Activities, Feeds, Attachments, or Content, mastering polymorphic relationships is a must.